The research disciplines whose use I advocate include inference, learning, and optimization. The aim is to model, design, and optimize different types of systems. There are numerous thrust areas of my research group.
The following samples a few key thrusts of my research, with selected publications in each area.Machine Learning for Physical Layer
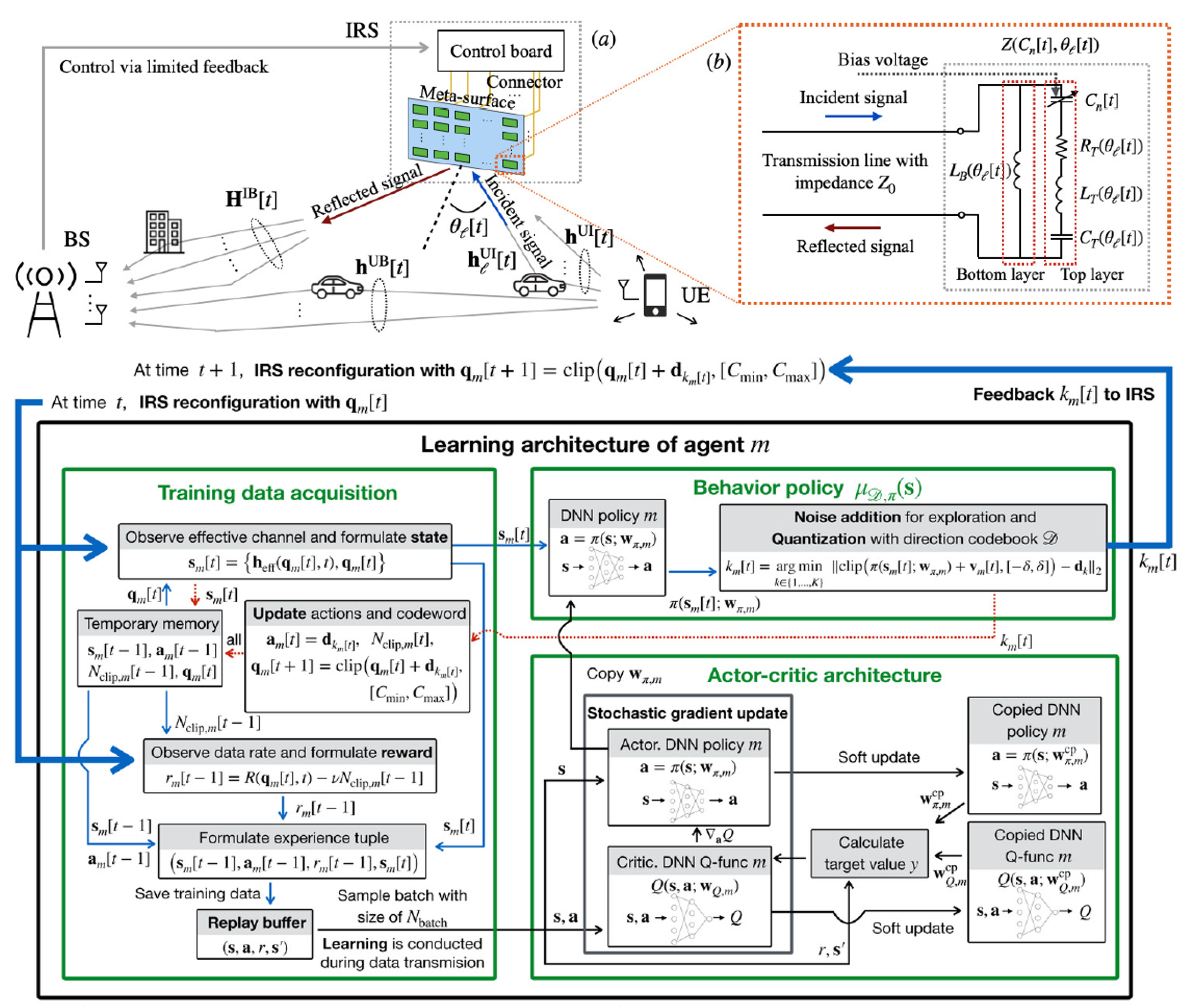
Traditionally, physical layer algorithm design was based on accurate linear system models. Information theory has played a central role in motivating the use of adaptation to improve spectrum efficiency drastically. Recently, AI/ML-based physical layer design has received substantial attention due to its exploitation of existing data and simple addon solutions. However, instead of making analytical contributions to understanding AI/ML-based physical layer techniques, many existing AI/ML-based approaches throw away the theory while relying heavily on training.
Of particular interest are optimization methodologies that engage performance insights to understand the fundamental limits of simple AI/ML-based physical layer techniques. We engage information theory, coding theory, and optimization theory to quantify data-driven enhancement to theory-based physical layer techniques. We have been looked at possible avenues for approaching “previously unsolvable problems” in signal processing and information theory such as IRS control, denoising, channel output feedback capacity, and approximate message passing problems to be addressed by AI/ML techniques.
Related Publications
- J. Kim, T. Kim, D. J. Love, and C. G. Brinton, "Robust Non-Linear Feedback Coding via Power-Constrained Deep Learning", International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2023.
- M. S. Oh, A. B. Das, S. Hosseinalipour, T. Kim, D. J. Love, and C. G. Brinton, "A Decentralized Pilot Assignment Methodology for Scalable O-RAN Cell-Free Massive MIMO," submitted to IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2023.
- J. Kim, S. Hosseinalipour, A. C. Marcum, T. Kim, D. J. Love, and C. G. Brinton, "Learning-based Adaptive IRS Control with Limited Feedback Codebooks," IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022.
- Q. Duan, T. Kim, and H. Ghauch, "KM Learning for Millimeter-Wave Beam Alignment and Tracking: Predictability and Interpretability," IEEE ACCESS, Aug 2021.
- M. S. Oh, S. Hosseinalipour, T. Kim, C. G. Brinton, and D. J. Love, "Channel Estimation via Successive Denoising in MIMO OFDM Systems: A Reinforcement Learning Approach," IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Montreal, Canada, June, 2021.
Feature Learning and Unsupervied Domain Adaptation
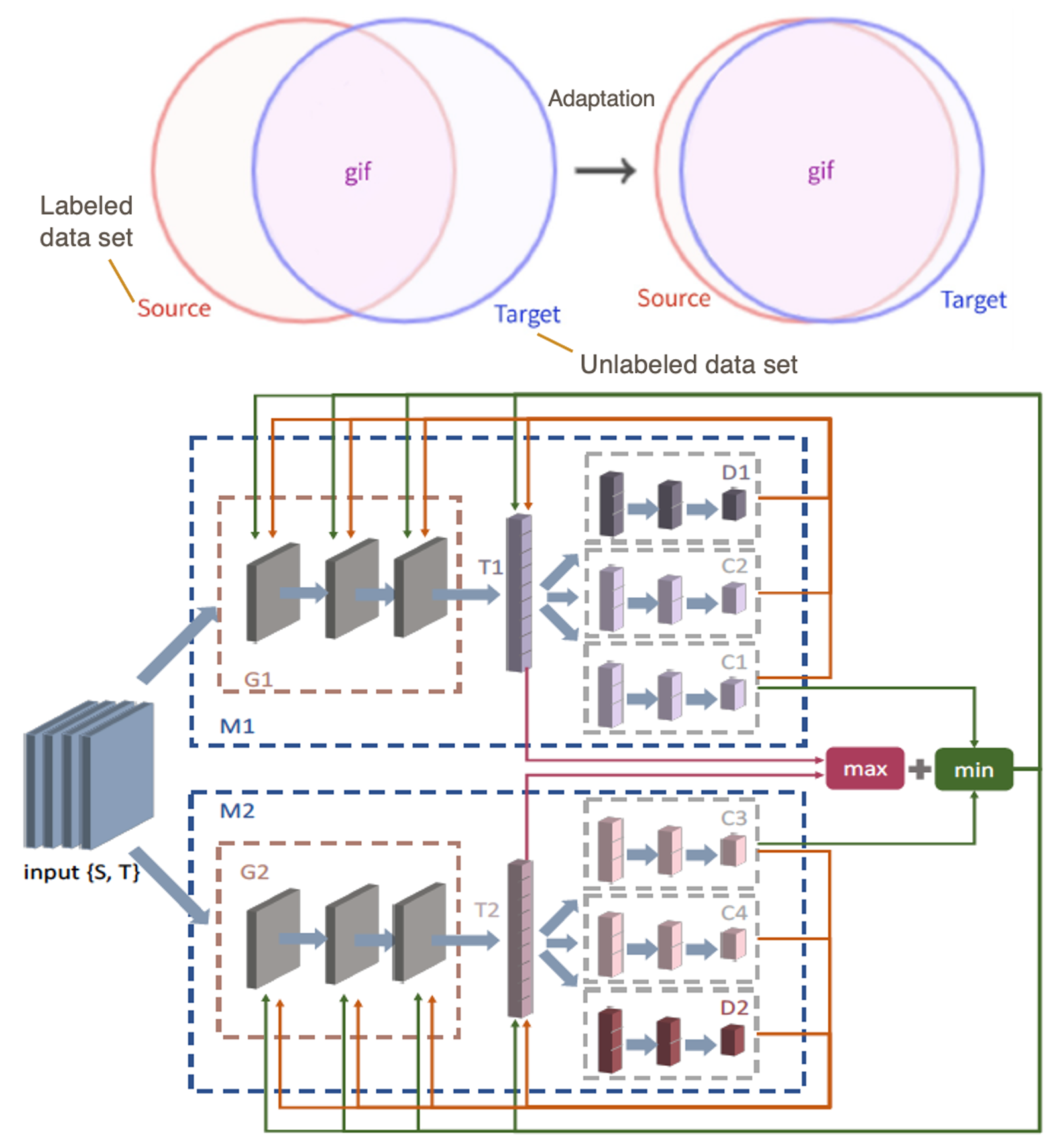
We propose a dual-module network architecture that employs a domain discriminative feature module to encourage the domain invariant feature module to learn more domain invariant features. This technique can be applied to any model that utilizes domain invariant features for unsupervised domain adaptation to improve its ability to extract domain invariant features.
Kolmogorov model (KM) learning has recently received great attention from source separation community due to its interpretability (in terms of extracting additional information or insights that are hidden inside the data) and predictive power. we for the first time enabled the application of KM learning in “big data” regimes, something that was previously impractical. The contributions are also applicable to a large family of data sets with missing entries.
Related Publications
- Q. Duan, H. Ghauch, and T. Kim, "Dual Optimization for Kolmogorov Model Learning Using Enhanced Gradient Descent", IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, Jan 2022.
- Q. Duan, T. Kim, and H. Ghauch, "KM Learning for Millimeter-Wave Beam Alignment and Tracking: Predictability and Interpretability," IEEE ACCESS, Aug 2021.
- Y. Yang, G. Li, T. Kim, G. Wang, "An Unsupervised Domain Adaptation Model based on Dual-module Adversarial Training", Neurocomputing, Dec 2021.
Millimeter Wave, Tera Hertz Hybrid Precoding and Channel Estimation
The so-called “beam alignment” is a procedure for finding the best transmit-and-receive beam pair to establish a link without estimating the channel state information (CSI). However, the use of directional narrow beams for searching the entire beam space is an extremely time-consuming operation.
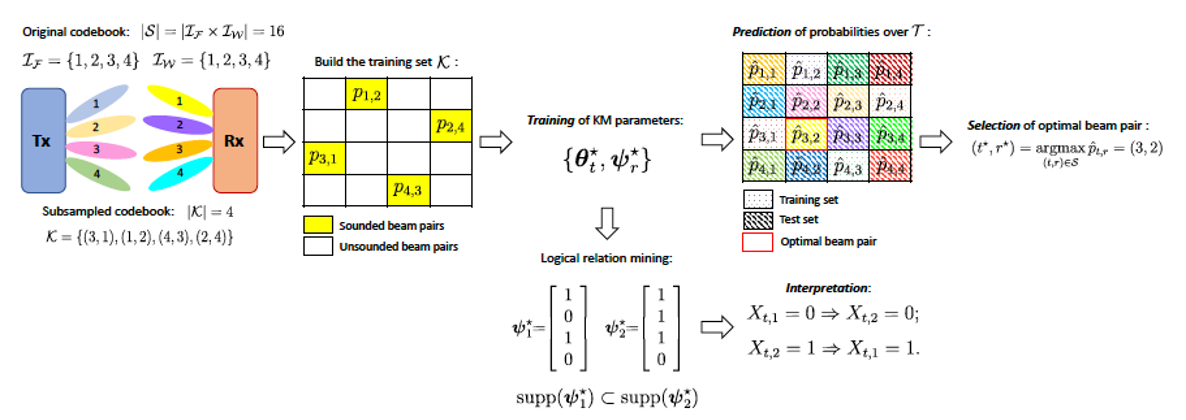
In this thrust area, we have been focusing on developing theories and algorithms for the purpose of achieving fast beam alignment and tracking (refinement) performance by leveraging advanced channel representation on virtual beamspace, unit probability simplex, Krylov subspace, and restricted isometry. Recently, the emphasis has been placed on the learnability and interpretability of the beam refinement process and its time-varying causality with CSI estimation.
Related Publications
- D. Q. Nguyen and T. Kim, "True-Time Delay-Based Hybrid Precoding Under Time Delay Constraints in Wideband THz Massive MIMO Systems," submitted to IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2023.
- W. Zhang, M. Dong, and T. Kim, "MMV-Based Sequential AoA and AoD Estimation for Millimeter Wave MIMO Channels," IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022.
- W. Zhang, T. Kim, and S. H. Leung, "A Sequential Subspace Method for Millimeter Wave MIMO Channel Estimation," IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 69, no. 5, pp. 5355-5368, April 2020.
- W. Zhang, T. Kim, D. J. Love, and E. Perrins, "Leveraging the Restricted Isometry Property: Improved Low-Rank Subspace Decomposition for Hybrid Millimeter-Wave Systems," IEEE Transactions on Communications, vol. 66, no. 11, pp. 5814-5827, Nov 2018.
- H. Ghauch, T. Kim, M. Bengtsson, and M. Skoglund, "Subspace Estimation and Decomposition for Large Millimeter-Wave MIMO Systems," IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 528-542, April 2016.
- S. Hur, T. Kim, D. J. Love, J. V. Krogmeier, T. A. Thomas, and A. Ghosh, "Millimeter Wave Beamforming for Wireless Backhaul and Access in Small-Cell Networks," IEEE Transactions on Communications, vol. 61, no. 10, pp. 4391-4403, October 2013. (TCOM Best Paper Award 2016, Stephen O. Rice Prize)
Distributed Interference Management, Resource Allocation, and Edge Computing
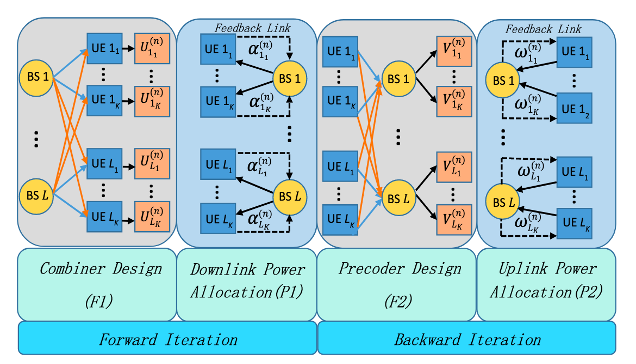
In this thurst, we have been developing distributed interference mitigation and resource allocation algorithms for multicell multiuser (MCMU) networks. The focus is providing performance guarantees with the minimum possible resource utilization. This thrust has been providng sufficient conditions for the feasibility of the proposed distributed algorithms by developing precoding, combining, power control, subchannel allocation, and relay selection frameworks. The underlying principle is decomposing the origianl sum rate maximization or performance-guranteed power minimization problems into forward and backward (FB) subproblems to ensure desired properites of the original problems such as strong duality, convexity, and convergence.
Related Publications
- J. Kim, T. Kim, M. Hashemi, C. G. Brinton, and D. J. Love, "Minimum Overhead Beamforming and Resource Allocation in D2D Edge Networks", IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2022.
- G. Xiong, T. Kim, D. J. Love, and E. Perrins, "Optimality Conditions of Performance-Guaranteed Power Minimization in MIMO Networks: A Distributed Algorithm and Its Feasibility," IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 69, pp. 119-135, Nov 2021.
- H. Ghauch, T. Kim, M. Bengtsson, and M. Skoglund, "Sum-rate Maximization in Sub-28 GHz Millimeter-Wave MIMO Interfering Networks," IEEE Journal of Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 35, no. 7, pp. 1649-1662, July 2017.
- H. Ghauch, T. Kim, M. Bengtsson, and M. Skoglund, "Distributed Low-Overhead Schemes for Multi-stream MIMO Interference Channels," IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 63, no. 07. 1737-1749, April 2015.
- T. Kim and M. Dong, "An Iterative Hungarian Method to Joint Relay Selection and Resource Allocation for D2D Communications," IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, vol. 03, no. 06, pp. 625-628, December 2014.
High Frequency Network Planning
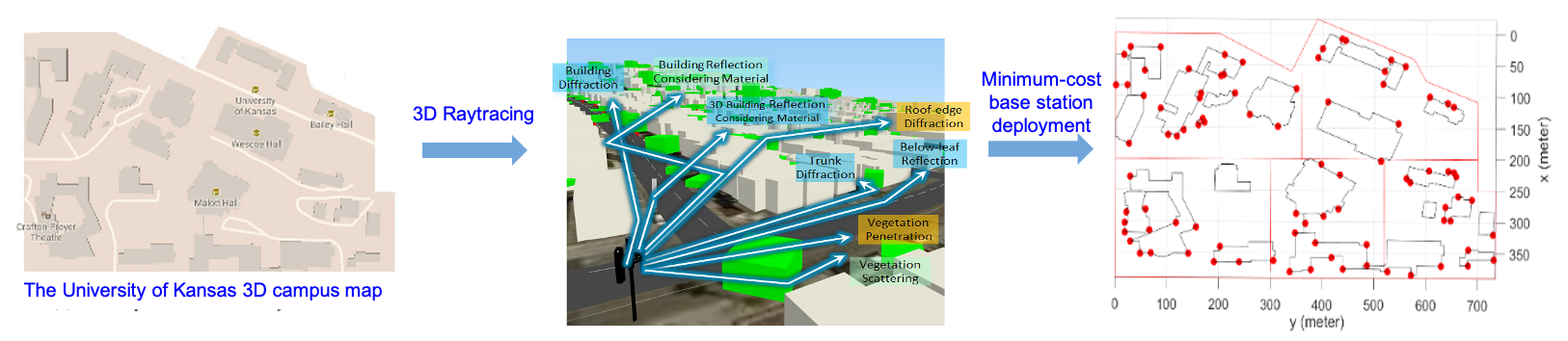
Although mmWave cellular systems can carry a larger volume of traffic, the recent increase in the cost of deploying and maintaining mmWave small-cell BSs is a practical concern that wireless service providers are constantly facing.
My group has been studying methodologies to the problem of mmWave BS deployment in urban environments by minimizing BS deployment cost subject to BS association and user equipment (UE) outage constraints by integrating physical blockage, UE access-limited blockage, and signal-to-interference-plus-noise-ratio (SINR) outage into its quantification. Interestingly, the proposed methods produce a unique distribution of the macro-diversity orders over the network that is distinct from other benchmark deployments.
Related Publications
- M. Dong, M. Cho, K. Lee, S. Yoon, and T. Kim, "Cost-Optimal Deployment of Millimeter-Wave Base Stations Under Outage Requirement", IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022.
- M. Dong, T. Kim, J. Wu, and E. Wong, "Millimeter-Wave Base Station Deployment Using the Scenario Sampling Approach," IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 69, no. 11, pp. 14013-14018, Nov. 2020.
- M. Dong, T. Kim, J. Wu, and E. Wong, "Cost-Efficient Millimeter Wave Base Station Deployment in Manhattan-Type Geometry," IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 149959-149970, October 2019.
- M. Dong and T. Kim, "Interference Analysis for Millimeter Wave Networks with Geometry-Dependent First-Order Reflections," IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 67, no. 12, pp. 12404-12409, , Dec 2018.
Algorithms on Manifolds
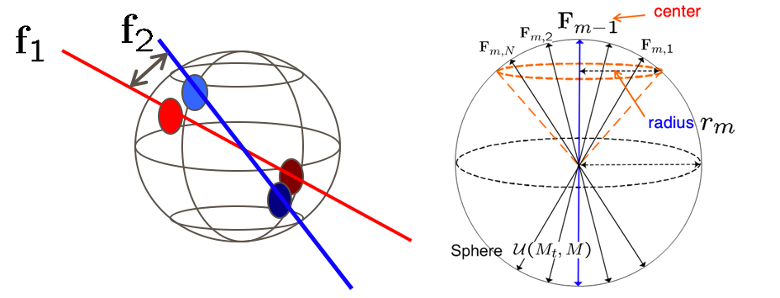
My group has been focusing on developing theories and methodologies for representing large-dimensional multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) channels on lower-dimensional subspaces by engaging manifold structure. Many algorithms on manifold bring expressiveness and accountability benefits, which can be used for developing optimized methods with considerably reduced complexity. My research has successfully engaged various manifold structures (Grassmannian, Riemannian, unit-simplex, etc.) for MIMO precoding, beamforming, channel estimation, and detection.
Related Publications
- Q. Duan, H. Ghauch, and T. Kim, "Dual Optimization for Kolmogorov Model Learning Using Enhanced Gradient Descent", IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, Jan 2022.
- Q. Duan, T. Kim, D. Lin, and E. Perrins, "Coherence Statistics of Structured Random Ensembles and Support Detection Bounds for OMP," IEEE Signal Processing Letters, vol. 26, no. 11, pp. 1638 - 1642, September 2019.
- W. Zhang, T. Kim, D. J. Love, and E. Perrins, "Leveraging the Restricted Isometry Property: Improved Low-Rank Subspace Decomposition for Hybrid Millimeter-Wave Systems," IEEE Transactions on Communications, vol. 66, no. 11, pp. 5814-5827, Nov 2018.
- T. Kim, D. J. Love, and B. Clerckx, "MIMO Systems with Limited Rate Differential Feedback in Slow Varying Channels," IEEE Transactions on Communications, vol. 59, no. 03, pp. 1175-1189, March 2011.
- T. Kim, D. J. Love, and B. Clerckx, "Does Frequent Low Resolution Feedback Outperform Infrequent High Resolution Feedback for Multiple Antenna Beamforming Systems?," IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 59, no. 04, pp. 1654-1669, April 2011.
- T. Kim, B. Clerckx, D. J. Love, and S. Kim, "Limited Feedback Beamforming Systems for Dual-Polarized MIMO Channels," IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, vol.9, no.11, pp. 3425-3439, November 2010.